Fenton Reaction: A Brief Overview
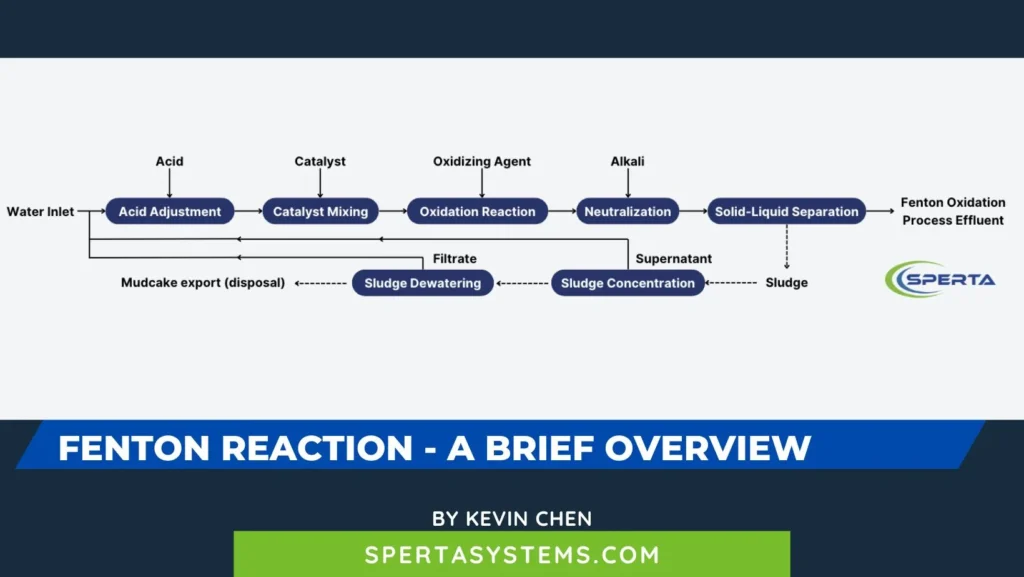
In 1893, chemist Fenton HJ discovered that a mixture of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and ferrous ions (Fe2+) exhibited strong oxidizing properties, capable of oxidizing many known organic compounds such as carboxylic acids, alcohols, and esters to inorganic states, with remarkable oxidation effects.
What Causes Sludge Floatation in Secondary Clarifier Tank?

The main factors influencing sludge floatation in secondary clarifiers include water quantity and quality, temperature, pH value, dissolved oxygen, and sludge retention time.
What is Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) and How is it Calculated?

Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) is a term used in water treatment processes, referring to the average time that wastewater remains in a reactor, essentially the average reaction time between the wastewater and the microorganisms in the biological reactor.
How to Calculate the Head of the Pump?

The pump head represents the height at which the pump can raise water, a key performance parameter also known as the pressure head. It can be expressed as the increase in fluid’s pressure head, kinetic head, and potential head, i.e.,
H=(p2-p1)/ρg+(v2²-v1²)/2g+z2-z1
SV30 in Wastewater Treatment – A Detailed Observation Guide

The Sludge Volume Index (SV) is a crucial indicator in the wastewater treatment process. It refers to the percentage volume occupied by sludge in a measuring cylinder after allowing the mixed liquor from the aeration tank to settle for 30 minutes.
Total Phosphorus (TP) Exceedance – Causes and Solutions

Denitrification and phosphorus removal processes are increasingly common in wastewater treatment. However, exceeding Total Phosphorus (TP) levels in the treated water often brings challenges during operational practice.

